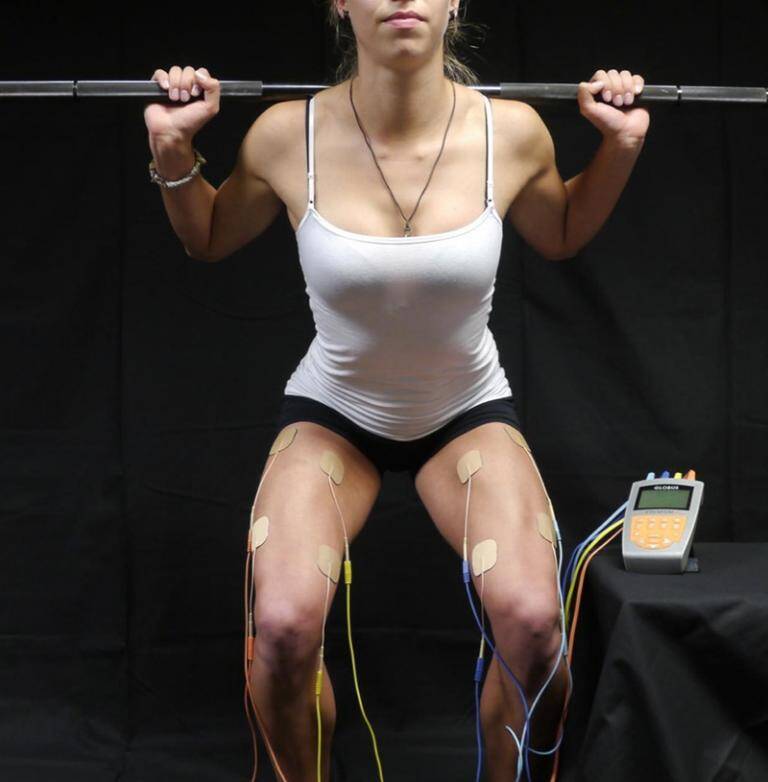
There can be a significant difference between muscle stimulations. The effect on the muscle depends on the settings of the impulse. In this article, I will walk you through how to combine exercise and muscle stimulation. Thankfully, with newer devices, you just select the disease (e.g. muscular atrophy, tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome) or the treatment goal (pain reduction, oedema reduction, muscle recovery, cramp prevention) from the menu and the device’s program “knows” the correct settings. Nothing needs to be adjusted, yet the most appropriate treatment can be given. Let’s look at the main programmes for athletes.
Briefly on muscle stimulation
Before you start electrically stimulating your muscles, you need to understand that it works completely differently than traditional exercise. You can find it here in more detail: basics of muscle stimulation.
In conventional training, the development of muscle fibres can be controlled by the load dosage. With this method, you can stimulate fast fibres II, for example, to a limited extent. This is because these fibres are only activated when a heavy load is applied – this is under neural control, so you can’t train each fibre type in isolation.
In the case of muscle stimulation, the frequency of the pulses determines the effect of the treatment to the greatest extent (pulse duration and current also play a role). It is, therefore, possible, for example, to hypertrophy the muscles (by stimulating fibres II.b), but this does not improve the condition of fibres I and IIa.
The right mix of training types
A simulation training programme should be designed to adjust the ratio of low frequencies “training” fibre I (endurance strength and aerobic endurance programmes), medium frequencies “specific” to fibre IIa (endurance strength programme) and maximum strength and hypertrophy programmes “tuning” fibre IIb.
If you overdo hypertrophy, muscle mass will increase but endurance, stamina and blood flow will not change, so you will not get performance improvements with more muscle.
However, if you only do endurance programs, the overall condition of the muscle will improve, but not the maximum strength and even more so not the muscle mass.
The correct definition of “mix” is the “science of stimulation”. It depends on the individual muscular endowment and, more importantly, the goals to be achieved.
For example, if you are an endurance athlete, frequent use of a hypertrophy programme will impair endurance (because it will result in an increase in IIb fibres, which are strong but not endurance). However, all IIa and IIb stimulation is also needed by the distance runner, as it will be used to “push” the last few hundred metres of the sprint, for example. If you don’t train the II fibres, there is no end speed-increasing effect either. That is, you can do a steady pace, but not a short acceleration from it.
Training programmes for muscle stimulation
When you buy a sports muscle stimulator, you’ll come across similar program names across all devices. Regarding the training schedule and electrode placement.
Warm-up:
A short-duration program that raises the temperature of the muscle in order to prepare it for exercise. Induces gentle, twitch-like muscle contractions that stimulate blood flow and muscle metabolism, raising the temperature. Muscle and ligament stiffness is reduced. The programme thus develops the ideal physiological muscle and tendon condition for exercise.
In case of injury treatment, it is beneficial to improve blood circulation. Improved circulation brings oxygen and nutrient-rich blood and at the same time removes metabolites and toxins produced by the injury.
Pre-Competition Warm-up:
It is longer lasting and deeper in effect than the PreCompetition Warm-up programme. It should be used a few minutes before the pre-competition warm-up on the muscles most affected by the sport. If you train on a daily basis, use this instead of the “regular” Warm-up.
In case of injury treatment, it is beneficial to improve blood circulation. Improved circulation brings oxygen and nutrient-rich blood while removing metabolites and toxins from the injury.
Capillarisation:
This programme is recommended primarily for endurance sports but is recommended for everyone in the first weeks of physical preparation. In Senzon, use only in endurance sports!
It stimulates blood flow to the muscle, improves oxygenation and reduces fatigue during hard physical work.
Helps activate the primary and secondary capillary system to improve tissue oxygenation and reduce fatigue during hard physical work.
Resistance:
Recommended for endurance sports; improves long-term, high-level muscle endurance, and reduces fatigue by preparing against metabolite formation.
After injury, it starts treatments to regain muscle strength.
Endurance:
Recommended for sports such as kayaking, middle-distance running (800-1500m), and martial arts, where the muscle has to work at maximum effort for a few minutes in an anaerobic (oxygen-deprived) state. It improves the muscle’s ability to exert high levels of effort over long distances; it helps to protect against toxin formation (acidification), reducing fatigue. Long intense muscle contractions are followed by short active rest periods.
Aerobic resistance:
Improves the ability to sustain a given effort over a long period of time. Long-duration stimulation programme adapted to improve the aerobic capacity of slow fibres.
You can use it after injury, but I recommend it if you have already completed 10-14 days of Endurance Strength training.
Hypertrophy:
Can be used to increase muscle mass. The high-frequency pulses result in intense muscle work, which is paramount in increasing the size of muscle fibres. Advantage: it can be focused on an important muscle or muscle group, i.e. you can selectively train the weakest points.
After muscle injury, use this programme only after full recovery.
Maximum strength:
Recommended for those requiring a high level of strength, such as in martial arts. Improves the ability to exert maximum force and increases muscle mass. It also helps to reduce the possibility of trauma during training with maximum weights.
After muscle injury, use this program only after full recovery.
Reactivity:
Optimum for ball games and combat sports. Improves the speed of contraction. Muscle stimulations are short, extremely intense and extremely fast. It acts on reactivity in two ways: by accelerating the contraction of fast fibres and by increasing the activity of myotactic receptors.
After muscle injury, use this program only after full recovery.
Explosive strength:
Used for sports performed at maximum force (e.g. short distance running, jumping and throwing sports, volleyball, etc.). It increases the mass of muscle fibres that can be “deployed” in the shortest possible time and at the highest possible force level.
After muscle injury, use this program only after full recovery.
Muscle Stimulation Training Programs for Rest and Recovery
Studies have shown that regenerative stimulation initiated within 90 minutes of physical activity reduces muscle lactic acid levels by about 25-40%. Perhaps only compression ice massage is more effective. The advantage of muscle stimulation, however, is that it is small and easy to use, so you can simply use it anywhere, anytime, as opposed to the hundreds of thousands of dollars of compression and ice massage machines.
- Active recovery: Recommended for all sports, especially recommended for multiple daily workouts. It stimulates muscle recovery, stimulates blood flow and reduces fatigue. It accelerates the flushing of metabolites and lactic acid from the muscles more effectively than traditional resting, allowing the intensity of successive workouts to be maintained at a high level. Particularly recommended for series workloads, such as the break between two halves, and the rest between two wrestling matches.
- Post-contest recovery: Longer and therefore more intense than the Active Recovery programme. It is recommended in all sports, after any training or competition. It promotes the flushing of metabolites, helping to overcome muscle fatigue.
- Relieving fatigue: This programme can be used whenever you need to rest a muscle that has become stiff from exercise. It provides muscle relaxation and stimulates blood circulation (which helps remove waste products)
How do you choose your treatment programme?
Whatever your goal, do a warm-up program on the muscle group of the  highest importance before each workout or competition.
highest importance before each workout or competition.
If your goal is to increase endurance, then the
- Use the Capillarization, Endurance and Aerobic Endurance programs in your workouts
- DO NOT use Hypertrophy, Maximum Strength, or Explosiveness programs because the high-frequency pulses stimulate IIa and IIb (fast) fibres – this improves strength but impairs endurance.
If your goal is to increase strength and muscle mass, and improve your speed and reflexes, then
- Use Hypertrophy, Maximum Strength, and Explosiveness in your training.
- You should use the Capillarization, Endurance and Aerobic Endurance programs because these low-frequency pulses mainly develop fibre I and to a lesser extent fibre IIa – this improves endurance but does not significantly change muscle mass, maximum strength or explosiveness.
Without exception, after every workout, perform a muscle regeneration treatment on the muscle groups most used during that session!
You can ask me for help in choosing the best equipment for your goals and integrating it into your training plan by e-mail, by writing a comment to this article or even by phone.
Which devices do you find these primers in?
You’ll find them all in the Globus range of devices for athletes. The “Champion” is basically an all-inclusive device. On the other hand, there are dedicated devices for specific sports like running, cycling, triathlon or football.
[message title=”The Champion” title_color=”#ffffff” title_bg=”#1e73be” title_icon=”” content_color=”#000000″ content_bg=”#ededed” id=””]
- Specific programs for preparation, development, prevention, recovery

- 90 specific development programs for 11 sports:
- Running, Swimming, Bicycling, Football,
- Skiing, Volleyball, Golf, Fitness sports,
- Triathlon, Skiing, Tennis
- Multifunctional electrotherapy device
- TENS | EMS, NMES, FES | MENS, MCR | Iontophoresis
- Max. 4 channels (8 electrodes)
[/message]
[message title=”Cycling Pro” title_color=”#ffffff” title_bg=”#1e73be” title_icon=”” content_color=”#000000″ content_bg=”#ededed” id=””]
- Multifunctional electrotherapy device

- TENS | EMS, NMES, FES | MENS, MCR | Iontophoresis
- Max. 4 channels (8 electrodes)
[/message]
All of them are multifunctional, i.e. they provide several types of electrotherapy treatments, such as TENS | EMS | MENS | MCR | FES | Iontophoresis currents.
The “basis” of each device is the same. These more than 100 basic programs ensure that you can use it to treat, repair, cure or prevent thousands of problems.
- Disease management: pain relief, muscle condition improvement, inflammation reduction, circulation improvement, oedema reduction, incontinence management, deep drug delivery, post-operative rehabilitation
- Sport preparation and muscle recovery, injury treatment and prevention programmes
- Fitness and fitness programmes. Weight loss support, post-pregnancy recovery
- Beauty care by improving muscle condition and skin elasticity. Professional microcurrent skin treatment programmes.
The name “sports” refers to the specific added value of the device, which provides programmes to prepare for competitions in this sport, treating and preventing typical injuries.
- Cycling Pro: any discipline of cycling
- Runner Pro: for running enthusiasts
- Soccer Pro: footballers
- Triathlon Pro: triathletes, including swimming, cycling and running
- The Champion: for multiple sports (Running, Swimming, Cycling, Football, Skiing, Cross Country, Volleyball, Golf, Martial Arts, Triathlon, Sailing, Tennis